High-Temperature Stainless Steel Ball & Butterfly Valves for Die Temperature Machines
High-Temperature Stainless Steel Ball & Butterfly Valves for Die Temperature Machines
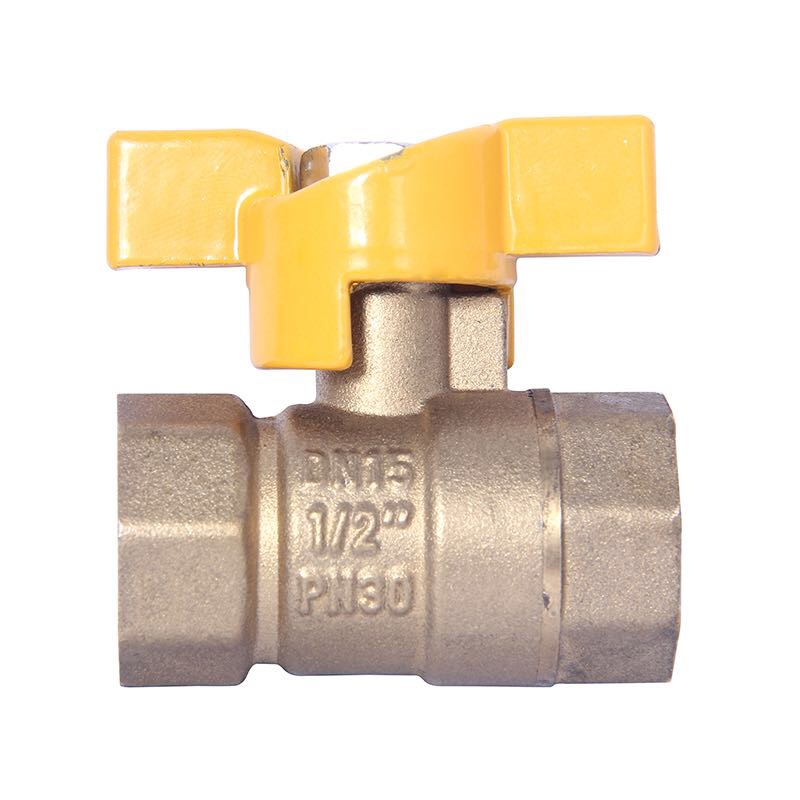
Precision-engineered stainless steel ball valve designed for extreme thermal environments in die temperature control systems.
When Industry Meets the Extreme: Fluid Control Challenges in High Heat
In die casting and injection molding, where molten metal or polymer flows at temperatures exceeding 300°C, a single point of failure can trigger a cascade of production disasters. Uncontrolled heat transfer leads to inconsistent mold temperatures, warping parts, increasing scrap rates, and even catastrophic tooling damage. At the heart of this thermal battlefield lies an often-underestimated component—the valve. More than just a flow switch, it stands as the frontline guardian of process stability. In these punishing conditions, standard valves buckle under thermal stress, seal degradation, and mechanical fatigue. The result? Leaks, jams, unplanned downtime, and spiraling costs. To master the heat, you need more than durability—you need intelligent engineering built into every turn of the handle.
More Than Just an On/Off Switch: How Stainless Steel Ball Valves Redefine Thermal Stability
A high-performance ball valve is not merely a gatekeeper—it's a precision instrument engineered to maintain laminar flow under extreme thermal cycling. Full-bore design eliminates flow restrictions, minimizing turbulence and pressure drop across the system. This becomes critical when handling thermally sensitive media like hot oil or glycol mixtures, where even slight friction can induce localized overheating. Constructed from 316L stainless steel, these valves resist corrosion and retain structural integrity far beyond carbon steel counterparts. While conventional carbon steel valves begin to creep and deform above 250°C—often failing catastrophically during rapid cooldown—316L maintains its strength due to superior chromium, nickel, and molybdenum content. Real-world comparisons show that while carbon steel valves exhibit micro-cracking after just weeks of operation at elevated temperatures, their stainless equivalents operate reliably for years.

Compact high-temperature butterfly valve integrated into a dense piping configuration for efficient thermal regulation.
The Agile Dance of Heat: Butterfly Valves Revolutionizing Mold Temperature Control
Where space is tight and response time matters, butterfly valves shine. In complex die temperature machines, compactness isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity. Mid-center and double-offset designs offer distinct advantages in frequent cycling applications. While mid-center models provide cost-effective sealing with lower torque requirements, double-offset variants reduce seat wear by minimizing contact during opening and closing, dramatically extending service life. The choice between elastomeric and metal-seated seals hinges on thermal expansion dynamics. Standard EPDM or FKM seals degrade rapidly above 200°C, whereas metal-to-metal sealing paired with high-temperature alloys ensures resilience up to 400°C. These lightweight yet robust actuators enable faster response times, making them ideal for dynamic temperature modulation loops that demand millisecond-level precision.
Decoding the Genetic Code of Heat Resistance: From Material Science to Microstructure
True endurance begins at the atomic level. One of the silent killers of stainless steel components is intergranular corrosion—a phenomenon triggered when chromium carbides precipitate along grain boundaries during improper heat treatment. The solution? Full solution annealing. By heating the material to 1050°C and quenching rapidly, we redistribute chromium uniformly, restoring corrosion resistance. Meanwhile, PTFE-based seat materials face their own Achilles’ heel: molecular chain scission. Above 260°C, PTFE begins to decompose, releasing harmful gases and compromising seal integrity. Advanced filled PTFE composites delay this breakdown, but only up to a point. For sustained performance near 300°C, hybrid fillers like glass fiber or graphite become essential. Add to this a passivated surface layer—achieved through nitric acid treatments—that forms an invisible oxide shield against oxidation, and you have a valve that ages gracefully, not prematurely.
The Synchronized Performance of Pressure and Temperature: Validating Seal Reliability Under Fire
Lab tests mimic real-world chaos. Imagine a valve subjected to 500 cycles per day, alternating between 320°C heat and sudden water-cooling bursts. After 10,000 cycles, infrared imaging reveals “hot spots” around the stem packing zone—areas prone to heat accumulation known as “thermal dead corners.” Traditional gland packings fail here first, allowing fugitive emissions. In contrast, multi-layer graphite wound seals not only withstand the heat but also self-lubricate under compression. Leakage rate data tells the story: standard packing shows detectable seepage within 2,000 cycles, while advanced graphite solutions remain hermetic beyond 15,000 cycles. This isn’t just about compliance—it’s about protecting personnel, environment, and product quality.

Internal view showing advanced graphite-filled sealing system designed for long-term performance under thermal cycling.
The Silent Guardian: How One Valve Can Decide the Fate of an Entire Production Line
Consider a Tier-1 automotive parts manufacturer where a single seized ball valve caused a complete shutdown of a $2.3 million die-casting cell. The root cause? A non-certified valve failed open during a weekend cooldown cycle, flooding the mold with cold oil and inducing severe thermal shock. The resulting crack rendered the tool unusable. Downtime stretched to 72 hours; losses surpassed $850,000. This wasn't just equipment failure—it was a systemic oversight. Today’s smart maintenance strategies integrate predictive lifespan algorithms that monitor actuation count, temperature exposure, and cycle frequency to forecast replacement windows before failure occurs.
The Future Is Intelligent: The Evolution of Smart High-Temperature Valves
Tomorrow’s valves won’t just endure—they’ll communicate. Prototypes now embed miniature RTD sensors directly into the body, transmitting real-time temperature data to SCADA systems. Paired with digital twin simulations, engineers can model valve behavior under fluctuating loads, optimizing selection based on actual plant conditions rather than theoretical specs. Emerging designs feature adaptive thermal expansion joints that automatically adjust clearance gaps during heating phases, eliminating manual re-torquing. This convergence of sensing, simulation, and self-adjustment marks the dawn of truly autonomous fluid control.
The Art of Choosing: Balancing Performance, Cost, and Risk
Selecting the right valve demands insight beyond catalog numbers. Overlooking factors like viscosity changes at startup or differential pressure spikes can lead to undersized actuators or premature erosion. Avoid common pitfalls such as assuming all "high-temp" labels are equal or neglecting stem load calculations in vertical installations. When evaluating butterfly valves, use a simple decision tree: start with maximum operating temperature, then assess cycle frequency, followed by required leakage class. Finally, during commissioning, perform three critical checks in the first five minutes: verify alignment between actuator and disc, confirm smooth handwheel operation without binding, and inspect for any visible gaps in flange connections. These moments save months of future troubleshooting.Choose wisely—not just for today’s heat, but for the longevity of your entire production ecosystem.




